
Free Windows RDP in 2025: Risks, Limits, and Safe Alternatives
If you’re evaluating Free Windows RDP in 2025, treat it like any other untrusted compute resource on the internet: assume hostile tenancy, unknown provenance, and zero assurance on patch level, identity controls, and telemetry. Most “Free Windows RDP” endpoints are either time-boxed trials, shared desktops, or recycled/compromised hosts posted publicly for anyone to use.
This guide breaks down the operational and security risks, typical resource and policy limits, and safer patterns that deliver the same outcome (remote Windows GUI access) with an acceptable risk profile.
What “Free Windows RDP” usually is
In practice, Free Windows RDP sources tend to be:
-
Legit trials from cloud/hosting vendors (often limited hours, low specs, region constraints)
-
Shared RDS hosts with multiple interactive users (no tenant isolation guarantees)
-
Credential dumps where accounts are posted publicly (almost always compromised)
-
Gray/illegal builds (unlicensed Windows, “activated” images, policy-violating setups)
The core issue is that you don’t own the identity plane, you don’t control the endpoint security posture, and you can’t validate the integrity of the OS image. With Free Windows RDP, you also inherit the reputation of the IP, which may already be on blocklists due to previous abuse.
Threat model: what can go wrong
A sysadmin view of Free Windows RDP starts with a basic assumption: the host is not trustworthy, and other users may be present.
1) Credential interception and token theft
Even if you avoid typing passwords, modern workflows leak secrets via browser sessions, OAuth tokens, clipboard sync, password managers, SSH keys, and cached credentials. On a hostile Free Windows RDP box, assume:
-
Keystroke logging is trivial
-
Clipboard is observable (and often logged)
-
Browser profiles and cookies can be dumped
-
“Free” admin accounts can be backdoored (scheduled tasks, WMI persistence, Run keys)
2) Malicious resident tooling
Shared Free Windows RDP instances commonly run:
-
Crypto miners (resource contention plus malware risk)
-
Proxy/relay tooling (your session rides alongside illicit traffic)
-
Credential stuffing/bot frameworks (high chance the IP is flagged)
Even if you only “download a file and leave,” you’ve still executed untrusted code paths in an untrusted environment.
3) Lateral exposure and client risk
RDP is a mature protocol, but the attack surface includes the client and its feature set (drive redirection, printer redirection, clipboard, dynamic virtual channels). Connecting to random Free Windows RDP servers expands your risk envelope because you’re engaging with unknown protocol behavior and server-side configuration.
4) Audit/compliance failure
If you touch customer data, production credentials, or regulated material, Free Windows RDP breaks typical controls: asset inventory, patch reporting, EDR coverage, centralized logging, and incident response. “We don’t know who owned the box” is not an acceptable post-incident statement.
Buy Cheap Dedicated Server Only $49.99/m
Operational limits you will hit
Even “non-malicious” Free Windows RDP is operationally painful:
-
Session caps: forced logoff, idle timeouts, concurrent session limits
-
No admin: blocked MSI installs, driver installs, PowerShell constrained language mode in some setups
-
I/O throttling: slow disk, capped bandwidth, high latency
-
Feature restrictions: clipboard/file transfer disabled, drive redirection blocked, printer redirection blocked
-
Non-persistence: profiles wiped at reboot; scheduled tasks removed; snapshots rolled back
These constraints often defeat the original reason people look for Free Windows RDP (repeatable work and persistent tooling).
Safe alternatives to Free Windows RDP
If your requirement is “Windows GUI + remote access,” you can achieve it without the risk profile of Free Windows RDP.
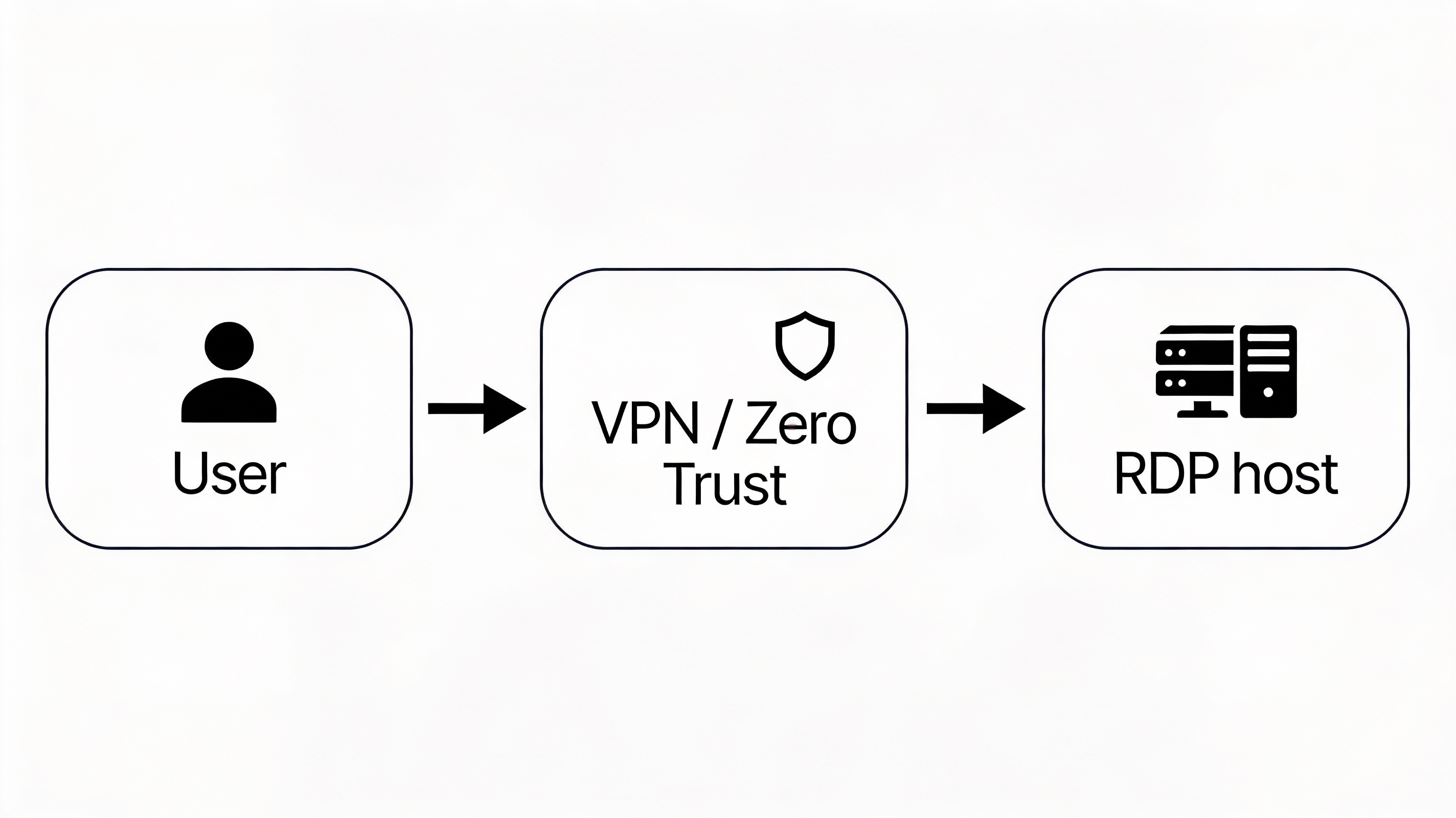
1) Self-hosted Windows + VPN (preferred)
Run Windows on your own endpoint (desktop, NUC, homelab) or a trusted VPS, then expose access only through a secure access layer:
-
WireGuard/OpenVPN (simple, robust)
-
A Zero Trust access proxy (policy-based access, device posture checks)
-
A hardened bastion/jump host pattern
This keeps RDP off the public internet and gives you control over patching, EDR, and local policy. It also lets you enforce per-user accounts and logon auditing.
2) Cloud PC / Windows VPS from a reputable provider
A low-cost paid Windows VPS is frequently safer than Free Windows RDP because you control:
-
Firewall rules (allowlist your IPs)
-
Windows Update cadence
-
Local security policy and accounts
-
Logging and backups
3) Remote access tools (when you don’t need raw RDP)
If the objective is remote control rather than native RDP, use a tool that supports MFA, device approvals, and session logging. This reduces the temptation to use Free Windows RDP lists and typically avoids exposing 33893389 entirely.
If you must use RDP: hardening baseline (minimum viable)
If you operate RDP on assets you own (not random Free Windows RDP), implement a baseline:
-
No direct internet exposure: don’t publish 33893389; front it with VPN/secure gateway
-
Enable NLA: requires authentication before full session creation
-
Enforce MFA at the VPN/gateway or via an RDP-aware access solution
-
Restrict inbound: allowlist source IPs; block brute force at the edge
-
Disable risky redirections if not required: clipboard/drive/printer redirection
-
Patch discipline: monthly OS + client updates; track RDP-related advisories
-
Account hygiene: no shared admin; remove unused local admins; enforce lockout and strong password policy
-
Logging/monitoring: forward Security logs; alert on RDP logons, failures, new services, and scheduled tasks
This gives you the usability of RDP without inheriting the unknowns that come with Free Windows RDP.
Free Windows RDP in 2025 (FAQs)
Is Free Windows RDP ever acceptable for production work?
No. Treat it as untrusted compute with unknown monitoring and unknown patch level.
What’s the safest pattern for remote Windows admin access?
RDP behind VPN/Zero Trust + NLA + MFA + strict allowlists and logging.
Why not expose 33893389 with a strong password?
Because credential stuffing, brute force, and misconfigurations are common—and you still lose the “network boundary” control.
What’s the fastest safe alternative to Free Windows RDP?
A small paid Windows VPS with IP allowlisting plus VPN access, or a managed remote-access tool with MFA.


